Thermal metal siding is a type of metal panel product commonly used for building exteriors, and typically comprised of the following elements:
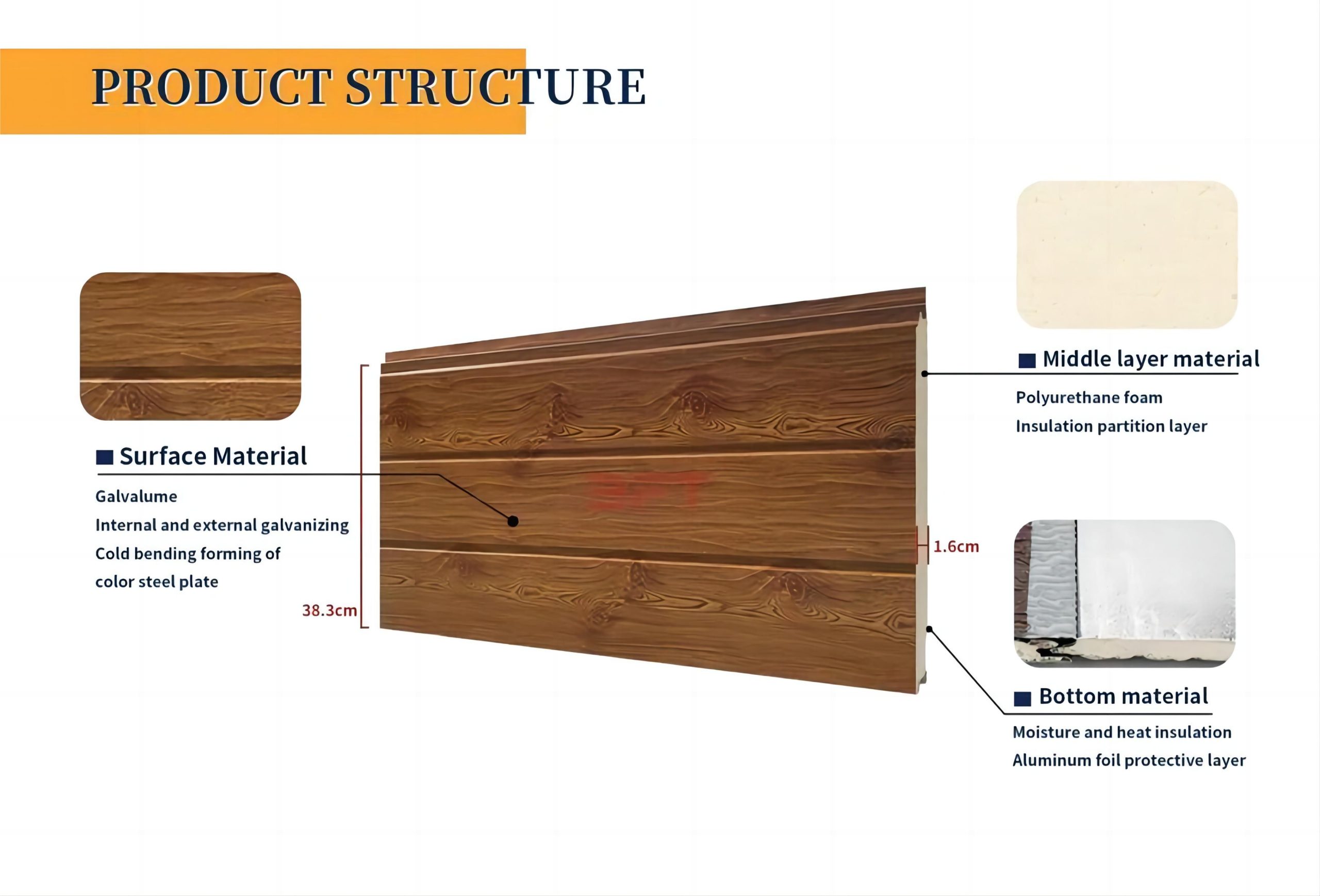
- Metal surface layer: typically constructed from materials like aluminum, zinc, magnesium, copper, among others, known for their outstanding corrosion resistance and durability.
- Coating: to enhance the weather resistance and visual appeal of the metal surface layer, coatings such as polyester, fluorocarbon, silicone, etc., are often applied to its surface.
- Insulation layer: employed to boost the building’s thermal insulation capabilities, an insulation layer is typically inserted between the metal surface layer and the back panel, with options like polystyrene, rock wool, glass wool, among others.
- Back panel: usually crafted from materials like galvanized steel sheet or aluminum sheet, the back panel is used to reinforce the product’s strength and rigidity.

Assembly method: Thermal metal siding is typically installed utilizing a hanging board technique, whereby one panel end is suspended on a support, with the other end connected to adjacent panels using a tongue-and-groove or locking joint.
Various materials and production methods for these components can be chosen and adapted based on specific application needs to meet the exterior aesthetic and thermal insulation requirements of various buildings.